Why data?
Place-based initiatives (PBIs) need to use data to help them understand and describe the issues in place, design and test initiatives, measure their impact, and report to communities and stakeholders, including funders.
This Fact Sheet was developed with and by leading place-based initiatives* as a part of the Data Catalyst Network, a network that brings together data experts of the Australian not-for-profit sector to collaborate and break cycles of disadvantage experienced by Australian youth.
The starting point is to guide practitioners in place on building a shared understanding of the ‘how to’ of accessing, collecting and using data for the purpose of shared measurement and shared decision-making.
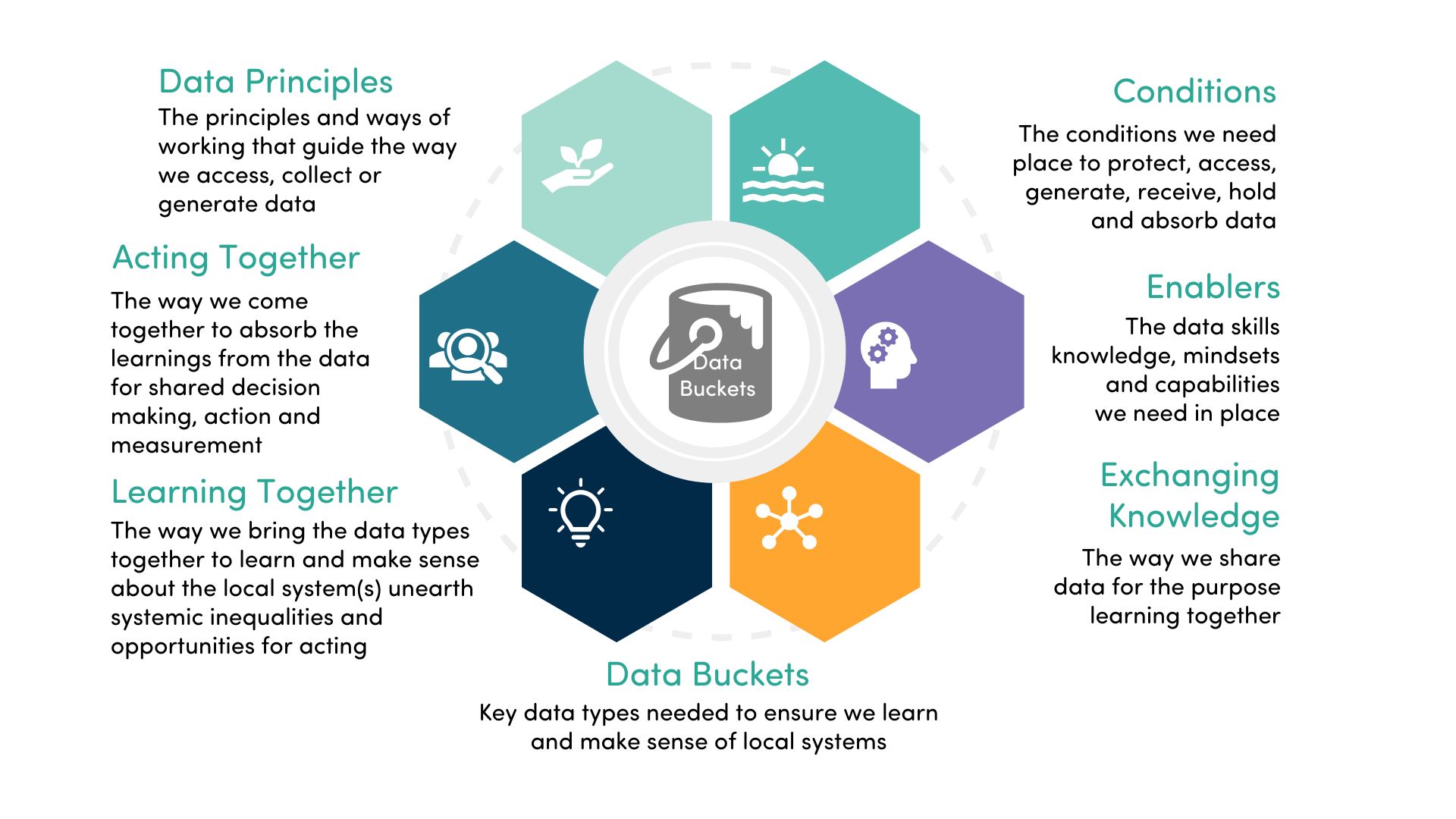
Below are the seven interconnected components and practices that support PBIs use data to share, learn, and act to enable shared decision making and measurement. These help PBIs to think about what they need to know about data.
Telling the Story or Problem Solving with Data
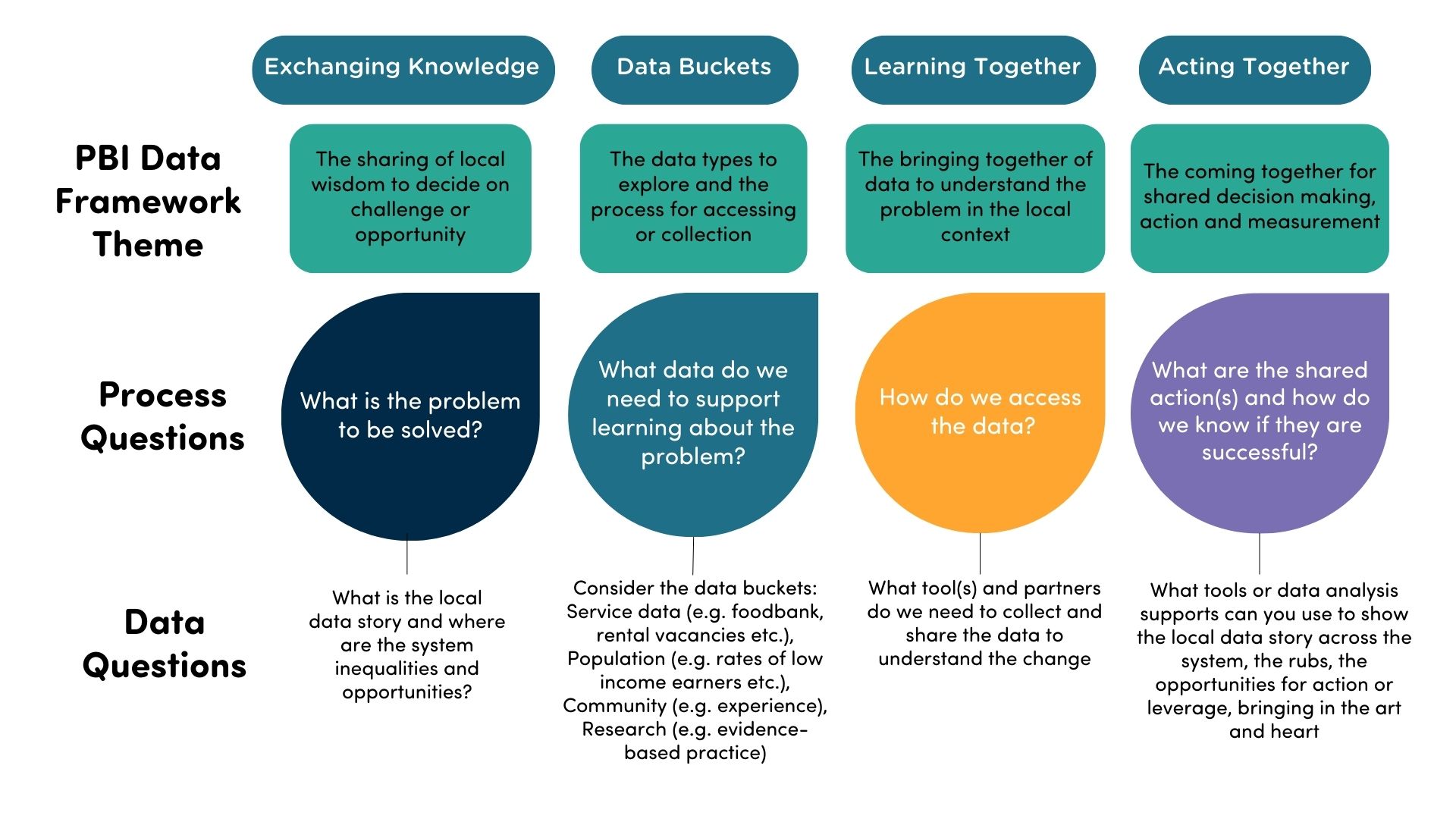
PBIs should begin by embedding their approach in a broader storytelling or ‘problem-solving’ framework.
The key to working with data is first identifying the challenge or opportunity the PBI is addressing, then thinking about what data is needed to understand the challenge, devise a plan, and share the results.
PBIs may be well placed to integrate complementary qualitative data and lived experience with broader population quantitative data, apprehend, and interpret local contexts and complex realities more accurately than external researchers.
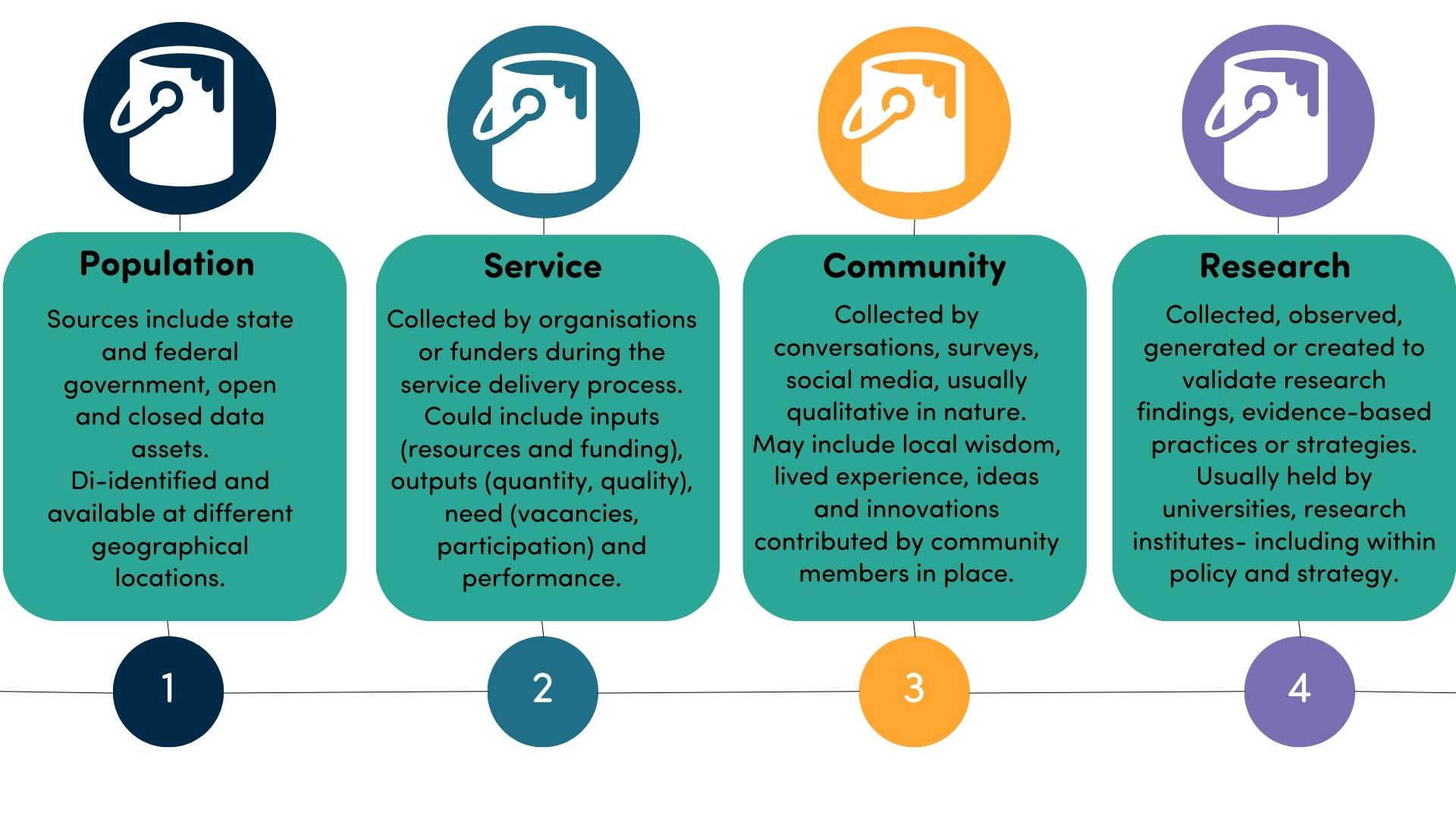
Data types
Most PBIs are accessing and using data, and they are also creating or sourcing techniques, tools, practices and resources to support them. Thinking about ‘data buckets’ helps to plan for shared measurement and decision-making.
Data Framework principles
Place-based data considerations to be included in a data framework.
|
Area |
What needs to be included in the framework |
|
Population Data Bucket |
|
|
Service Data Bucket |
|
|
Community Data Bucket |
|
|
Research Data Bucket |
|
|
Exchanging Knowledge |
|
|
Learning and Acting Together |
|
|
Principles |
|
|
Conditions |
|
|
Enablers |
|
Data framework resource links
These are the main national and Queensland resources to support PBIs in using data, identified in consultation with Queensland-based initiatives.
*We’d like to thank our partners for contributing to this resource, including Restacking the Odds, Logan Together, yourtown, Gladstone Region Engaging in Action Together, Mission Australia, Department of Treaty, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Partnerships, Community and the Arts, Childrens Health QLD, Nexus Foundation Partners, Griffith University, QCOSS, University of the Sunshine Coast, Infoxchange, Hand Heart Pocket, Department of Social Services, Department of Health, Brisbane North PHN Southern Moreton Bay Islands, SEER Data, Thriving Queensland Kids Partnerships.
Tools, techniques and resources that can support the use of data in place-based initiatives
|
Population Data Bucket Data Access and Platforms |
|
|
Population Data Bucket Indicators |
|
|
Service Data Buckets |
|
|
Community Data Bucket |
|
|
Research Data Bucket |
|
|
Exchanging Knowledge |
|
|
Learning and Acting Together |
|
|
Principles |
|
|
Conditions |
|
|
Enablers |
|
|
AI |
Learn about the full process involved in the creation of a tailored, place-based initiative framework
Find a comprehensive document that demonstrates the co-design process to build a data framework for place-based initiatives that will give you a deeper understanding of what place-based initiatives need to know about using data here.
Learn via case studies
Learn about place-based initiative frameworks from stories of success. Restacking the Odds has been supporting better outcomes for Logan's children and families. Read how they've facilitated shared decision-making and the principles of a shared framework.






Status message
Thanks for rating this guide.