Operating environments for not-for-profits (NFPs) are inherently complex and subject to various disruptions, from technological failures to natural disasters. Effective planning through Business Continuity Plans (BCPs) and Disaster Recovery Plans (DRPs) is essential to minimize the impact on operations and ensure the continued delivery of services.
What is a business continuity plan?
A Business Continuity Plan (BCP) outlines how an NFP will continue delivering critical services during and after a disruption. The core focus of a BCP is to maintain essential functions and services, with non-critical operations potentially suspended until full recovery.
Key elements of a Business Continuity Plan
- Critical Services Identification: Document the activities crucial for the delivery of key products and services.
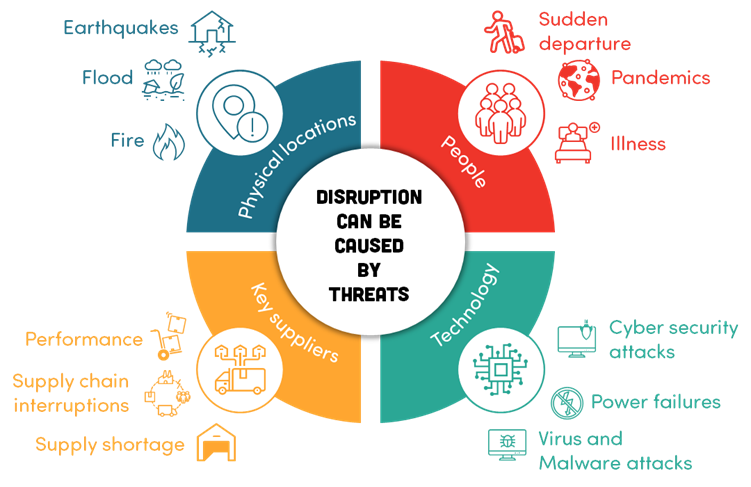
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential threats to these critical activities and outline contingency measures.
- Communication Strategies: Establish alternative communication channels for stakeholders including staff, suppliers, and clients.
- Alternative Resources: Detail backup equipment and service providers, along with any manual processes that may be required if digital systems fail.
Importance of a Business Continuity Plan
The COVID-19 pandemic exemplified the necessity for NFPs to adapt rapidly to maintain service continuity. A well-exercised BCP is not just a static document but a dynamic plan that involves regular updates and drills to ensure its effectiveness and to familiarize staff with emergency procedures.
What is a Disaster Recovery Plan?
A Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP), a subset of the BCP, focuses specifically on restoring IT and technological infrastructure after a disruption. It is crucial for recovering access to essential digital and communication systems.
Key Elements of a Disaster Recovery Plan
- Technology Recovery: Outline procedures for restoring critical technological systems, including servers, networks, and applications.
- Data Access: Ensure mechanisms are in place to recover and access critical data post-disruption.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Involve business stakeholders in defining recovery priorities, objectives, and timeframes.
Importance of a Disaster Recovery Plan
With NFP operations increasingly dependent on technology—from email communications to CRM systems—a DRP helps minimize the downtime and disruption caused by technological failures. Understanding the potential impacts of technology disruptions allows for better preparation and response strategies.
Maintaining your plans
- Regular Reviews: Both BCPs and DRPs should be reviewed regularly and updated to reflect organizational changes and new potential threats.
- Training and Drills: Conduct training sessions and simulation drills to ensure staff understand their roles during a disruption and to refine the plans based on practical insights.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Continuously engage with internal and external stakeholders to ensure the plans meet all necessary operational requirements.
For NFPs, having structured and well-maintained BCPs and DRPs is not just about risk management; it's about ensuring sustainability and the ability to fulfill their mission under any circumstances. By preparing for disruptions, NFPs can protect their stakeholders and maintain critical services even during unforeseen events.
Read next
For assistance in creating a disaster recovery plan, including a template you can customise, refer to our Intermediate level guide Creating an effective disaster recover plan




Status message
Thanks for rating this guide.